 Did you skip filing or request an extension on your 2021 taxes because you couldn’t pay? You have several options.
Did you skip filing or request an extension on your 2021 taxes because you couldn’t pay? You have several options.
It’s happened to many people at one time or another. You wait until the last minute to prepare and file your income taxes, only to receive a very unpleasant surprise: You owe money, and you don’t have it to give. Even if you file for an extension, the IRS still expects you to send in what you estimate you’ll owe. If that’s absolutely impossible, you should always try to send in what you can.
The first thing you should do, of course, is to review your 1040 again. Did you take all of the credits and deductions that you should have? Or make any calculation errors? Did you somehow overstate your income?
If after checking your return you still see that large number on line 37 (Amount you owe), try not to despair. And certainly, don’t neglect to file. Instead, take advantage of one of the many options you have.
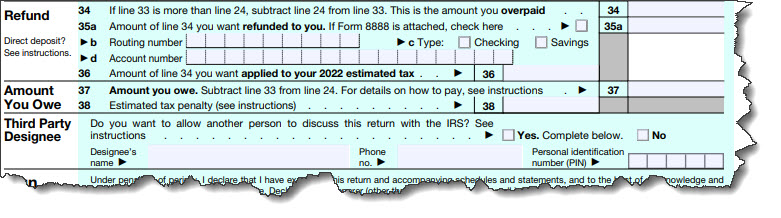
If you have to enter a big number on line 37 and you lack the funds to pay the IRS, there are several different steps you can take.
Try to Get a Loan
This is the best solution if it’s possible. Consider approaching family members who you know might have enough disposable income to help you out temporarily. If that’s not possible, check with your bank or credit union or online lenders. Paying interest may be more economical than dealing with IRS penalties and interest – and less harmful to your tax-paying history.
Set Up an Online Payment Plan
If you qualify (and most individual taxpayers do), you can set up an online payment plan through the IRS itself. You don’t have to contact the agency. It can all be done on the web. Once you’ve provided the required information, you’ll be notified immediately about your approval status. There are two types:
- Short-term payment plan. This is designed for taxpayers who owe less than $100,000 and are going to repay it in 180 days or fewer. Keep in mind that the late-payment penalty and interest will continue to accrue, so those amounts have to be figured into your plan. There are no other fees for this.
- Long-term payment plan. This is also known as an installment agreement, and it usually involves a setup fee, though low-income individuals might be able to have the fee waived or reimbursed. Your total debt to the IRS must be less than $50,000 (combined tax, interest, and penalties), and you’re required to make monthly payments. If you filed your return on time, your late-payment penalty will be reduced from up to 1 percent per month to 0.25 percent per month for as long as the installment agreement is in effect.
Offer in Compromise
It may be possible for you to settle your tax bill with the IRS and pay less than what you originally owed. There is a non-refundable fee of $200 that is generally waived for low-income taxpayers. You can see if you’re eligible by visiting this site and completing the multi-step questionnaire.

You can use this IRS tool to see if you pre-qualify for an Offer in Compromise, which could reduce your tax bill
Delayed Collection
If you are absolutely unable to pay and the IRS can confirm this, the agency may delay collection until your finances improve. Call the number on your notice to request this action, or call (800) 829-1040. Interest and penalties will continue to accrue during the delay.
Penalty Relief
You may also be able to get your late-payment penalties reduced or eliminated if you have reasonable cause, as defined by the IRS. The agency decides whether you’re eligible for this on a case-by-case basis. If you have a solid history of compliance, the First Time Abatement program may be available to you.
Planning Ahead Helps
It’s good to know that there are options if you can’t come up with enough money to pay your tax bill, but you can probably avoid that situation if you do year-round tax planning. Looking at your income and expenses—especially the major ones—in terms of their effect on your taxes can go a long way toward avoiding surprises at filing time. Let us know if we can help you develop such a strategy.
 As a small business owner, tax liability is the money you owe the government when your business generates income. With changing laws and gray areas regarding deductions, exemptions, and credits, it’s no wonder small business owners rank taxes at the top of the list of the most stress-inducing aspect of business ownership. To reduce that stress, taxes shouldn’t be something to focus on only at year’s end. Use these tips on reducing your business tax year-round and see your taxes and stress level decrease!
As a small business owner, tax liability is the money you owe the government when your business generates income. With changing laws and gray areas regarding deductions, exemptions, and credits, it’s no wonder small business owners rank taxes at the top of the list of the most stress-inducing aspect of business ownership. To reduce that stress, taxes shouldn’t be something to focus on only at year’s end. Use these tips on reducing your business tax year-round and see your taxes and stress level decrease! Comparing a business’s key financial ratios with industry standards and with its own past results can highlight trends and identify strengths and weaknesses in the business.
Comparing a business’s key financial ratios with industry standards and with its own past results can highlight trends and identify strengths and weaknesses in the business. It’s not just self-employed individuals who must pay estimated taxes. Here’s what you need to know.
It’s not just self-employed individuals who must pay estimated taxes. Here’s what you need to know.
 You may not think about taxes often, but they can prove to be a large expense. That’s why it’s important to make the most of any opportunities you may have to lower your tax liability. Here’s a look at some of the factors you may want to consider in your planning.
You may not think about taxes often, but they can prove to be a large expense. That’s why it’s important to make the most of any opportunities you may have to lower your tax liability. Here’s a look at some of the factors you may want to consider in your planning. There are always more things to learn about the applications we use every day. Here are some tips for expanding your use of QuickBooks Online.
There are always more things to learn about the applications we use every day. Here are some tips for expanding your use of QuickBooks Online.